Poster Presentation Australian Diabetes Society and the Australian Diabetes Educators Association Annual Scientific Meeting 2014
Basal Plus compared with Biphasic insulin in type 2 diabetes: A post-hoc, subset analysis of the Australian data from the LANSCAPE trial. (#327)
The LANSCAPE trial demonstrated that, in type 2 diabetes, after 24 weeks a Basal Plus regimen (insulin glargine [Lantus] once daily plus insulin glulisine [Apidra] at main meal) was non-inferior to a twice-daily Biphasic regimen (insulin aspart/aspart protamine 30/70 [NovoMix30]) with superior patient-reported outcomes.1 We undertook a sub-analysis of the Australian dataset.
At enrolment, participants’ mean (SD) age was 60.8 (7.61) years, diabetes duration was 14.4 (6.52) years and HbA1c was 8.5 (0.99)%. Participants meeting the inclusion criteria (fasting blood glucose <7.0 mmol/L and HbA1c >7.0%) after an 8-12 week run-in period during which oral agents except metformin were stopped and insulin glargine optimised were randomised to Basal Plus (N=46) or Biphasic (N=43) regimens.
At 24 weeks, HbA1c fell by 0.89% in the Basal Plus and 0.90% in the Biphasic arms; the least squares (LS) mean difference was -0.00004% (SE 0.17, upper 97.5% CL 0.35, p=1.00), adjusted for baseline HbA1c and baseline*treatment interaction. The difference in treatments was smaller in the Australian dataset than for the study overall (LS means difference 0.18, upper 97.5% CL 0.34).1 Exploratory analysis of the interaction between regimen and country did not find any significant between-country effects on change in HbA1c at week 24.
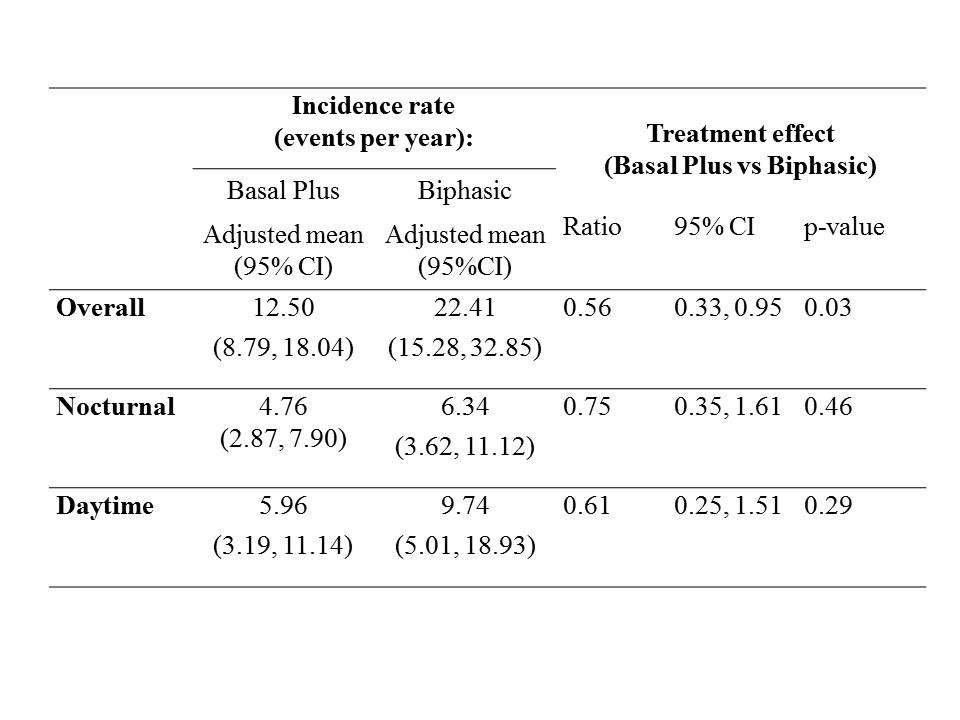
Overall (data not shown), and in the Australian cohort, there were significantly more hypoglycaemic events among participants in the Biphasic arm than the Basal Plus arm (Table); the rate of nocturnal hypoglycaemic events in each arm was not significantly different. There were 7 severe hypoglycaemic events; 6 of which were in the Biphasic arm (two participants had one event each; one participant had 4 events). Basal Plus provides an acceptable option for insulin initiation and/or intensification in type 2 diabetes.
Table: Hypoglycaemic event rates.
Financial support: Study funding and editorial support provided by Sanofi.
- Vora J et al. Diabetes, 2013;62 (Suppl 1A):p13LB [Abstract].