Poster Presentation Australian Diabetes Society and the Australian Diabetes Educators Association Annual Scientific Meeting 2014
New Insulin Glargine 300 U/mL: Glycaemic Control and Hypoglycaemia in a Meta-analysis of Phase 3a EDITION Clinical Trials in People with T2DM (#328)
The EDITION 1, 2 and 3 studies compared the efficacy and safety of new insulin glargine 300 U/mL (Gla-300) with insulin glargine 100 U/mL (Gla-100) in people with T2DM on basal and mealtime insulin, basal insulin and OADs, and no prior insulin, respectively.
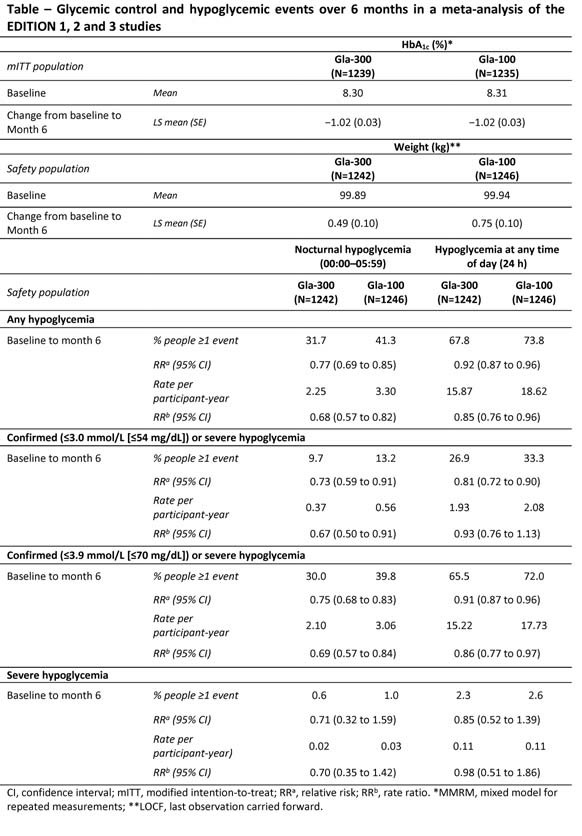
A meta-analysis of these three studies enabled glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia to be examined over 6 months in a large, heterogeneous T2DM population (Gla-300, N=1247; Gla-100, N=1249). Mean change in HbA1c was comparable for Gla-300 and Gla-100 (each −1.02 [SE 0.03] %). Gla-300 was associated with a reduced risk of experiencing a hypoglycaemic event vs Gla-100 (nocturnal and at any time of day; Table).
Rates of nocturnal hypoglycaemia were consistently lower with Gla-300 than Gla-100. Severe hypoglycaemia at any time of the day was rare in both treatment groups (2.3% with Gla-300 vs 2.6% with Gla-100). Weight gain with Gla-300 and Gla-100 was slight (mean change: 0.49 [SE 0.10] kg, 0.75 [0.10] kg, respectively), with a trend for less weight gain with Gla-300 (−0.26 [95% CI −0.52 to 0.01] kg, p=0.058).
In conclusion, Gla-300 provides comparable glycaemic control to Gla-100 in T2DM, with consistently less hypoglycaemia at any time of the day and less nocturnal hypoglycaemia.